1
Chinese yuan becomes most traded foreign currency on the Moscow Exchange, surpasses the US dollar
The Chinese yuan became the most traded currency on the Moscow Exchange for the first time on Monday, with trading turnover in the yuan-ruble pair reaching 70.3 billion rubles ($1.17 billion), surpassing the 68.2 billion rubles for the dollar-ruble pair, according to a report from Russian informational agency RosBiznesConsulting (RBC) on Wednesday. The report said a total of 64,900 transactions were made using the yuan-ruble pair, compared with 29,500 for the dollar-ruble pair on the same day. The yuan also overtook trading in the euro-ruble pair, which recorded a trading volume of 47.5 billion rubles. The popular status of the Chinese yuan on the Moscow Exchange remained unchanged on Tuesday, with volume of trading for the yuan-ruble pair reaching 63.9 billion rubles (in total 46,000 transactions), and that of the dollar-ruble pair standing at 59.4 billion rubles (21,500 transactions) as of close, according to a report from China Central Television on Wednesday. Yuan-denominated assets are gaining favor in the Russian market as bilateral trade has gained momentum over recent years. In the first eight months of 2022, trade between China and Russia totaled $117.2 billion, up 31.4 percent year-on-year, according to data from China’s General Administration of Customs. Shu Jueting, a Ministry of Commerce spokesperson, said on August 25 that bilateral trade between the two countries is maintaining strong growth momentum, and the two sides will continue to promote normal economic and trade exchanges and maintain stability of industrial and supply chains. In early September, China and Russia reportedly signed an agreement to switch trade payments for gas supplies to China to the yuan and the ruble based on a 50-50 split, instead of the dollar, paving the way for a more frequent ruble-yuan usage in bilateral trade. Outside of Russia, the yuan has also been increasingly used in global trade and settlements amid the steady internationalization of yuan and bullish global views on the long-term development momentum of the Chinese economy. According to data from global payment services the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), the Chinese yuan has retained its position as the fifth most active currency for global payments by value in August, accounting for a 2.31 percent share. In August, the overall amount of payment made with yuan jumped 9.25 percent month-on-month, SWIFT data showed. The latest report from IMF showed that the Chinese yuan accounted for 2.88 percent of global foreign currency reserves in the second quarter of 2022, ranking fifth worldwide and maintaining its highest global reading since data was first released in 2016. As the credibility and reputation of the US dollar system is at a higher risk of collapsing due to Washington’s irresponsible monetary policy, de-dollarization is viewed as a forthcoming global trend, with more markets likely to recognize the yuan's internationalization trend over the long run, Chen Jia, a research fellow with the International Monetary Institute of the Renmin University of China, told the Global Times on Wednesday. Media Source: Global Times
2 Chinese scientists successfully complete free-space dissemination of time and frequency with E-19 instability over 113 km Chinese scientists have realized the experiment on free-space high precision time and frequency dissemination across 113 kilometers for the first time in the world, with dissemination of time stability reaching the femtosecond level, which can meet the time dissemination requirements of the optical clock with the current highest precision. This achievement in basic scientific research is expected to have major applications in the study of fundamental problems in physics, from navigation, to gravitational wave detection, to dark matter search. The relevant results were published online on Wednesday night in the international academic journal Nature, according to Chinese media. The research was completed by the team of Pan Jianwei, China's leading quantum physicist at the University of Science and Technology of China and a Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) academician, together with cooperative institutes such as the Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Science and Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory. In recent years the frequency instability for state-of-the-art optical clocks has reached the E-19 level, which can be used in precision navigation and positioning, global timing, wide-area quantum communication and basic principles of physics and will play an important role in the field of physics. E-19 level means that a clock error is no more than one second in about 100 billion years, according to the report of the China News Service. "Precise timing should not be limited to cold laboratories, but should also 'fly into ordinary people's homes,'" said Shen Qi, the first author of the article and an associate researcher at the University of Science and Technology of China. The expert also noted that there should be a time dissemination technology that matches the accuracy of the optical clock to spread precise time. According to an abstract from the article, key technologies essential to this achievement include the deployment of high-power frequency combs, high-stability and high-efficiency optical transceiver systems and efficient linear optical sampling. The technique can not only be directly used in ground-based applications, but could also lay the groundwork for future satellite time-frequency dissemination. Media Source: Global Times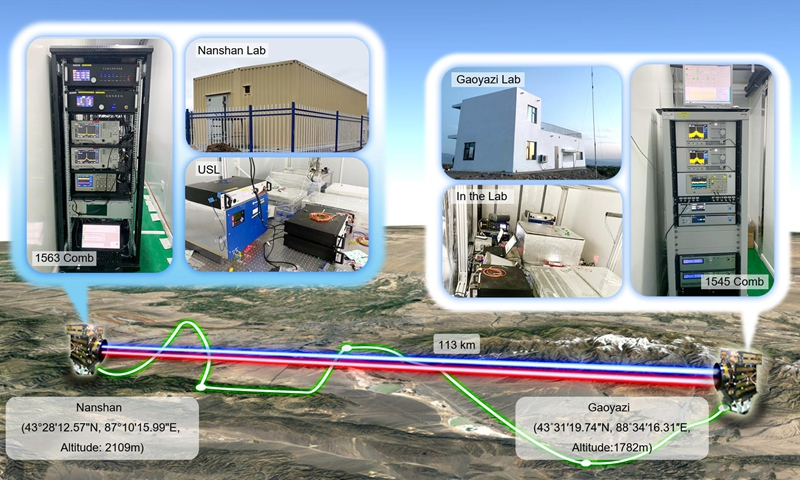
3 BYD’s EV sales surpass Tesla by nearly 200,000 in Q3, remains world’s top-selling EV manufacturer China's auto giant BYD has sold 537,164 units of new energy vehicles in the third quarter of this year, surpassing Tesla by nearly 200,000 vehicles and maintaining its position as the world's biggest electric vehicle producer by sales. According to data newly released by Tesla and BYD on Monday evening, Tesla's global sales were 343,830 vehicles in the third quarter, a year-on-year increase of 3 percent, which was lower than market expectations. Meanwhile, sales volume of BYD's new energy passenger vehicles was 537,164 units, a year-on-year jump of 187.01 percent. In September alone, BYD's new energy vehicle sales reached 201,259 units, compared with 71,099 units in the same period last year, a year-on-year surge of 249.56 percent, according to a filing it published on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange on Monday. BYD has for the first time dethroned Elon Musk's Tesla as the world's biggest electric vehicle producer by sales in the first half of the year, with global sales of 641,000 vehicles versus the 564,000 units sold by Tesla. The third quarter data, which showed a widened gap, demonstrated BYD has further consolidated its position as the world's biggest electric vehicle producer by sales, industry observers said. They noted that BYD's momentum also underscores China's strengthening position in renewable energy, boasting advantages across much of the supply chain for electric vehicles, batteries, wind as well as solar energy. From January to August, China's global market share of new energy passenger vehicles has increased to 68 percent, which was mainly driven by the strong demand for new energy in China, Cui Dongshu, secretary general of the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA), said in a post published on his WeChat account on Sunday. "In the face of the strong market demand, we asked some of our workers to come back earlier from the National Day holidays to ramp up for customers' orders," owner of an auto parts supplier in Nantong, East China's Jiangsu Province, told the Global Times on Wednesday. The owner, who asked to remain anonymous, said the company mainly provides car parts for new energy carmakers in Shanghai. "We have been working at full capacity since the coronavirus in Shanghai receded in June, orders have piled up until to the end of the year." At the same time, Chinese carmakers are also actively building vehicle production plants overseas to expand capacity and reduce transportation cost. BYD, for example, said on September 8 that it would build its first overseas passenger car plant in Thailand, wholly invested by the company. On September 16, Chinese electric-vehicle maker NIO celebrated the shipment of its first battery swap station from Biatorbagy, Hungary, to Germany, produced by NIO Power Europe, the company's first overseas plant. Media Source: Global Times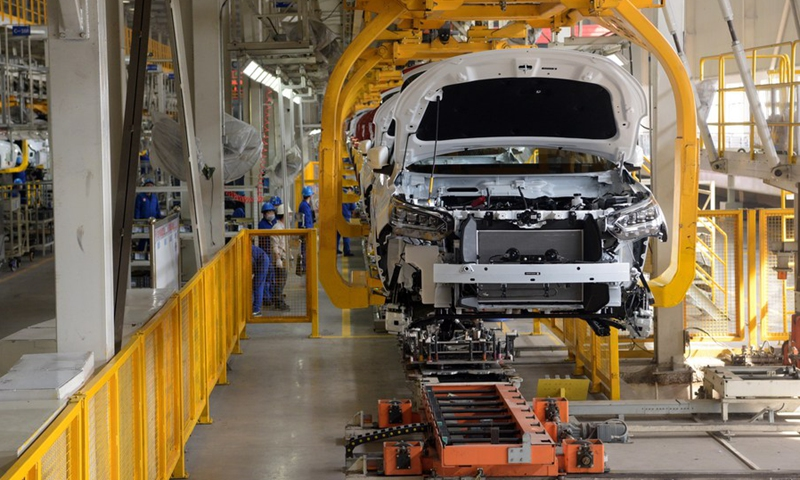
4 SABIC has chemistry with China's green goals As the main driver of global demand for industrial chemicals, China's green energy transition is expected to provide massive opportunities for major chemical corporations like SABIC, and the Saudi company vows to further facilitate China's transition toward sustainable development through an innovation-driven strategy, said a senior company executive. "SABIC will continue investing in innovation and technological development in China, a key strategic market for SABIC, as we have been doing during the past nearly four decades," said Bob Maughon, SABIC chief technology and sustainability officer, during an exclusive interview with China Daily. SABIC will continue supporting China in the realization of its carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals with lighter, more durable, long-lasting and recyclable materials in 5G communications, electric vehicles, packaging and photovoltaic power generation in the years to come, Maughon said. He said SABIC has been actively increasing the use of renewable energy in China and globally, which is a key part of SABIC's global roadmap to carbon neutrality. The company is also exploring opportunities in terms of technology options for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) applications in the country. Developments related to hydrogen are significant for China, which is the world's top hydrogen producer. China's ambition to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 also calls for lowering the carbon intensity of its hydrogen-production methods from the conventional "grey" to low-carbon blue and green, he said. Grey hydrogen is the hydrogen produced using fossil fuels whereas green hydrogen is hydrogen gas that is produced using renewable energy. Blue hydrogen occurs when natural gas is split into hydrogen and carbon dioxide, with CO2 captured and then stored. Currently, SABIC is working together with the China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation on CCUS studies to seek more technology options for CCUS applications in China. The company is also talking with local partners to identify new CCUS technologies and exploring potential opportunities together, he said. Luo Zuoxian, head of intelligence and research at the Sinopec Economics and Development Research Institute, said SABIC's commitment confirms China's massive potential in the CCUS sector, which has also been attracting more international players in recent years. For petrochemical companies, CCUS — which offers a way to reduce emissions from sectors that are hard to decarbonize — will not only help expand their own business but also allow them to become sustainable over the long run, Luo said. According to a report by Shell Plc, for China to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060, more than 1.3 gigatons of CO2 per year will need to be captured and permanently stored by then, which means CCUS capacity will need to increase more than 400-fold over the next four decades. China, with an estimated 2,400 gigatons of CO2 storage capacity, has significant geological potential for storing carbon, second only to the United States. It currently has more than 40 CCUS pilot projects with a total capacity of 3 million metric tons. Many of these projects are small developments linked to enhanced oil recovery that will need to significantly scale up over the next four decades, said the report. "China's high-level opening-up, including improving the business environment and expanding market access, has offered massive opportunities to multinational companies like SABIC in China. "China's intention to welcome more foreign investment is especially appealing for global companies like SABIC and we look forward to more academic cooperation with local partners," Maughon added. Media Source: China Daily
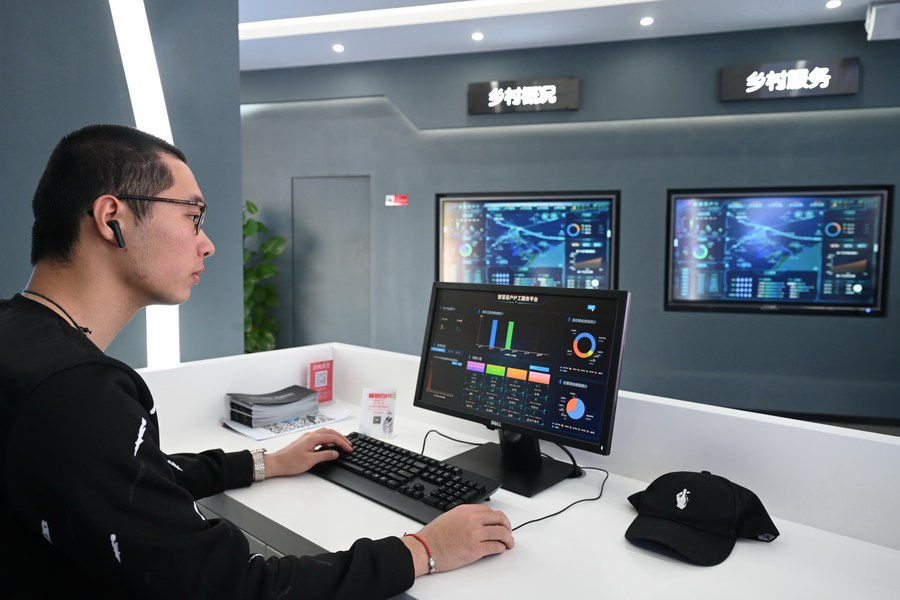
5 Digital transformation creates new types of employment in China Digital transformation and technological innovation have brought about new professions requiring new skills and knowledge in various industries amid China's endeavors to promote high-quality development. China has added 158 new professions to its list of recognized occupations since 2015, according to the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security. It started the revision work in April last year in order to update the edition released in 2015. This brings the total number of professions on the newly-revised list to 1,639, according to the ministry. Increased digital waves have affected the labor market in a variety of ways, for example, providing more types of work. The revised list identifies 97 professions related to the digital sectors. The move is designed to meet the employment demand of the booming digital economy and support its development, especially in technological innovation and talent team construction, said Wu Liduo, director of a technical guidance center for employment training of the ministry. A program has been launched to provide training for digital technology engineers, which covers about 80,000 people every year, said Li Jinsheng, an official with the ministry. China's digital economy grew at an average rate of 15.9 percent from 2012 to 2021. During the period, the share of the digital economy in its GDP expanded from 20.9 percent to 39.8 percent, representing an annual average increase of about 2.1 percentage points, according to a white paper on global digital economy released by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology. The latest edition of the list also features professions within the country's emerging industries such as cryptographic engineering, carbon management and financial technology. By adding the new types of jobs to the list, it is expected to boost the development of related industries, increase employment, and strengthen vocational education and training. In 1999, China published its first reference book on occupational classifications. In 2010, China started revising the reference book by adding new types of work and published the revised edition of the reference book in 2015. The ministry said efforts have been made to formulate national standards for new professions and launch occupational training courses to cultivate more talent. China has increased spending from its general public budget on improving people's livelihoods and keeping the job market stable this year. Expenditure on social security and employment totaled 2.53 trillion yuan (about 365.05 billion U.S. dollars) in the first eight months of 2022, up 6.6 percent year on year, data from the Ministry of Finance showed. Media Source: China Daily 